Digital Phone System Cost Guide
Find out all the costs related to a digital phone system for your house or apartment. Browse our Digital Phone System Cost Guide for more info!
Note: Communication technology uses many technical terms and abbreviations, which can be very confusing. We have tried to
minimize use of such terms, but inevitably we had to include a few of them. We have included a cheat sheet of terms at the end of this article.
The Digital Phone System
The digital phone is a phone that works with digital rather than analogue signals. The digital or VoIP phone system is a communication system that enables both data and voice signals to be exchanged between two end-points or terminals following a set of internet rules or protocols called internet protocol or IP. IP ensures that communication between two end points, usually a computer, phone, tablet, TV, fax, or other communication device, is done correctly and securely.
The digital phone system can be installed for the home or business as an upgrade of the analogue system. It serves as both internet and conventional phone system. The internet can be used to transmit voice in a digital format using the voice over IP or VoIP. VoIP enables a seamless transmission of voice and data packets. It also simplifies the office setup by using digital devices that can work with multimedia. One of the best attributes of the VoIP is that it enables making of regional and international calls cheaply (at local rates) using Microsoft Skype and Vonage World, who compare as follows;
| PROVIDER | COST | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| Vonage | $9.99- 27.99 | Easy and supported set up. Standard features include voicemail retrieve, caller ID, call block, 3-way calling, etc. Present in 60 countries. It has no video or text capabilities. |
| Skype | $2.99-13.99 | Many features including video calling and texting. Only requires a computer, headset and broadband. Present in 63 countries. It incompatible with 911 and hardware phones like Vonage. |
A Quick Cost Guide
Before installing the digital phone system you have to decide exactly what you need. Consult a telecommunications expert – unless you are a phone guru yourself. Identify a service provider who has an affordable plan that meets those needs satisfactorily, for example, if your system is primarily for voice communication or downloading multimedia files, then you will be consuming a lot of bandwidth. The cost of a digital system can be split into cost of equipment and monthly subscription.
Cost of Equipment
A set of equipment is required to set up the digital phone system. The table below shows some of the equipment and costs for an SMB and home digital phone system;
| EQUIPMENT/INSTALLATION | COST | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| PBX (4 to 12 Lines) | $200-$400 | For SMB |
| Virtual PBX | Free-$300 | |
| PBX Extension Line | $80 each | |
| Handset | $50-$200 | |
| Headset | $20-$350 | |
| VoIP Installation/connection | $20-$150 | |
| Ethernet | $400 | For home use |
| Skype-ready headset | $100-$170 | Hi fidelity with 24-bit output |
| Monthly Subscription per User | $3-$120 | |
| Phone/Network Installer per hour | $200 | |
| Power Backup (Battery) | $170-$400 | |
| Power backup (UPS) | $60-$150 |
Cost of Monthly Plans
All digital phone providers charge a monthly fee per user. The provider has a number of plans aimed at different segments of consumers. Below are some providers’ base rates for SMB and home users;
| PROVIDER | MONTHLY |
|---|---|
| 8x8 Virtual Office Pro | $24.99 |
| Adobe Connect | $50.00 |
| Amazon Chime | $15.00 |
| Broadvoice Cloud PBX | $22.95 |
| Cisco WebEx Meeting Center | $24.00 |
| ClickMeeting | $30.00 |
| Fonality Hosted PBX | $24.99 |
| GoToMeeting | $19.00 |
| Jive Hosted VoIP | $29.95 |
| join.me | Free |
| Microsoft Skype for Business | $2.99 |
| Ooma Telo – Amazon | $82.90 |
| Vonage Business | $81.92 |
| Zoho Meeting | $12.00 |
Cost of Headsets
When you use a softphone or virtual PBX, you may need to purchase a good quality headset to use in place of the computer’s built-in microphone and speaker system. Quality headsets are comfortable to wear, have noise reduction and cancellation, and give clear sound. Headsets vary greatly in cost and quality as shown in the following examples;
| HEADSET MODEL | COST |
|---|---|
| Audio-Technica ATR2500 | $100 |
| Blue Microphones Snowflake | $35 |
| Cisco-Linksys CIT300 | $139 |
| Grandstream GS-GXP2160 | $107 |
| Jabra Evolve 65 UC Stereo Wireless Bluetooth | $200 |
| Jabra 75 MS Stereo Bluetooth Headset | $260 |
| Logitech Clearchat | $26 |
| Logitech G35 | $93 |
| Logitech USB Headset Stereo H650e | $90 |
| Marshall Electronics MXL Studio | $170 |
| Philips 080 | $32 |
| Polycom VVX 500 | $189 |
| Samson Meteor Mic | $110 |
| Sennheiser PC363D | $256 |
Types of VoIP Digital Phones
A VoIP or IP phone can be classified into any of five categories, namely; conference phones, desktop phone, wireless phone, softphone, and cell phone. Common brand names are AT&T, Talkswtch, Cisco, Nortel, Polycom, and Panasonic. 8×8 and RingCentral have proprietary IP phones, while Nextiva, Vocalocity, and Apptix have SIP-based VoIP phones.
Conference Phone
The business conference phone can connect many users at the same time into a common session or conference. A variant, broadcast phone, can connect to thousands of users, mainly as listeners. Not all providers support business level conferencing. This system is expensive because it uses the top of the range equipment for clear sound and long microphone range. For example enterprise-grade headsets have noise cancellation, wideband, and UC compatibility.
Desktop Phone
These are the standard phones found on most office desks and at homes. They between $20 and $80 but high-end units that can take multiple calls simultaneously cost more than $400. Some VoIP provider give include them in the plan as offers. The desktop phone has the most built-in features like voicemail, call waiting, caller ID, directory, three-way calls, and so forth. They mostly do not require installation, just plug in the phone jack and use.
Wireless Phone
This is a cordless desktop handset that uses blue-tooth or infra-red technologies to transmit to a base station. It is not as full-featured as the corded desktop phone, but it is mobile within the base station’s range. It requires some setting up, especially to align it with the base station.
Softphone
The softphone is a software-driven VoIP system that is downloaded into a computer or as a smartphone and tablet app. You also need a headset. Microsoft Skype is a softphone. A softphone is affordable and sometimes free, and has many features for business and enterprise users.
Cell Phone
The cell phone (and tablet) is a convenient handheld communication that is used on the go. It has many advanced features that enable different modes of communication such as calls, video calls, three-way conference, text, chat, internet, and email. They can be loaded with softphone to enable VoIP.
VOIP System
The VoIP system works with a broadband internet to give value-added communication services. Voice quality depends on broadband. Basic features include auto-attendance, conferencing, voicemail, integration, caller ID, call hold and forward, social media support, multimedia, memory dialing, and so on. The full cost of installation is $4500, while the setup fee is $650, and the monthly maintenance cost is $600. The annual maintenance fee is $7200.
VoIP improves the home and SMB’s services at little or no extra cost. It is portable because you can access it from any internet point and relocate the office with it. They have many features, especially for integration, UC, virtual receptionist, and call center. It routes calls to extensions and virtual extensions alike. It allows detailed reporting. However, the system is interrupted when the broadband or internet are interrupted. It is also vulnerable to virus attacks. It does not dial emergency numbers because it is not based on a physical location.
Key System
The key system is designed for an SMB. It has a PBX with several lines and extensions. It has such features as call hold with music, paging, voicemail, memory dialing, and intercom. The system costs $3000 to install, $1700 to set up, and $600 for monthly maintenance. The annual maintenance cost is $6600.
It is compatible with traditional analogue wiring, which saves up to $1000 on wiring charges. It has a user-friendly interface represented by keys on the keypad. It is cheaper to maintain. It is however, less flexible, has few features, and not suited to conferencing. The number of supported lines and extensions is limited.
Before You Switch to the VoIP Digital Phone
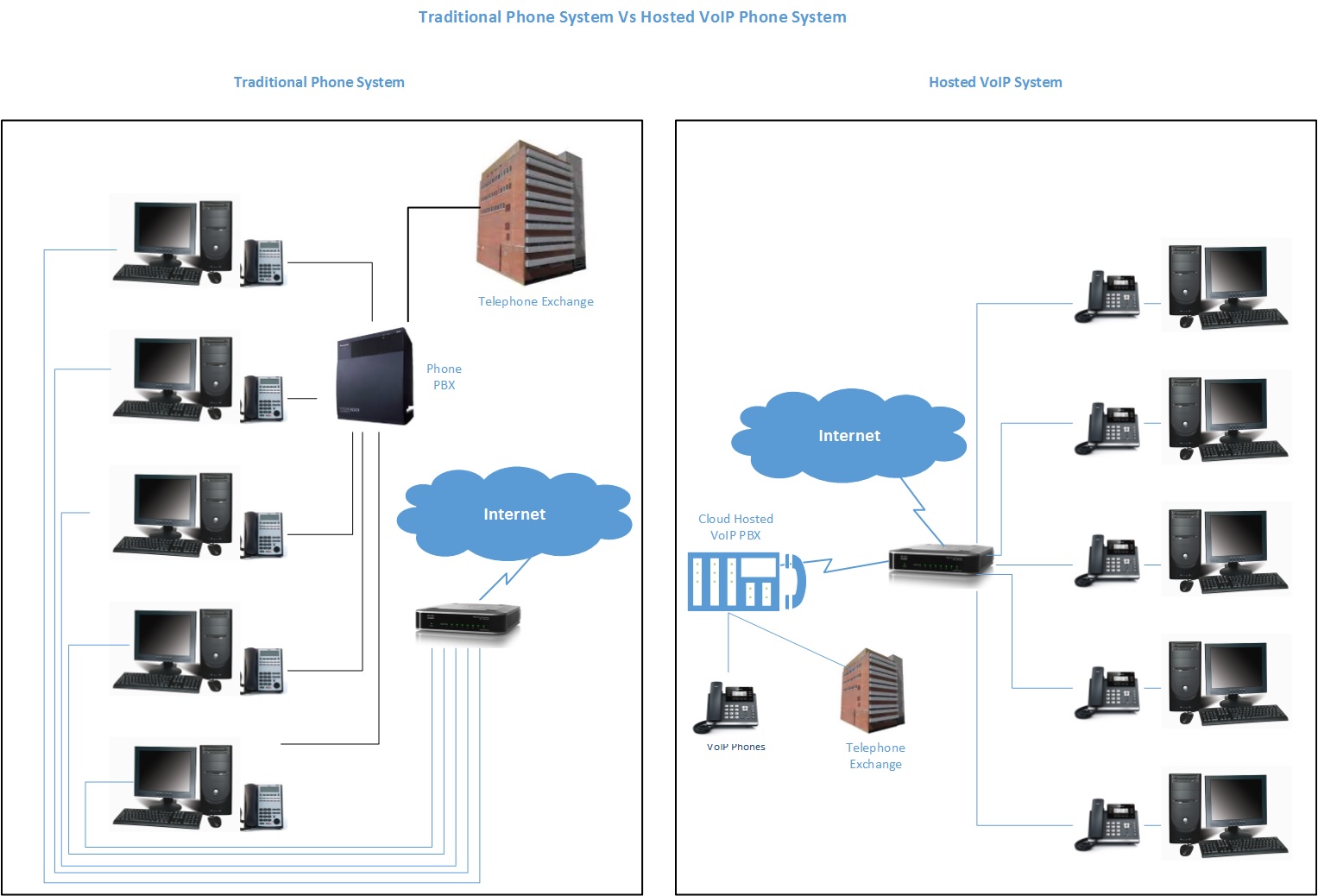
Homes and businesses need communication systems. The home requires the system for telephone, cable TV, and internet. Usually they will have a separate provider for each of these services, which can be costly, and so they need to find a VoIP service provider to give them a one-fits-all plan. Businesses need the system for telephone and internet services. Modern businesses have the services as a unified communication service.
POTS or PSTN
The plain ol’ telephone system or POTS is an analogue signal system that uses a pair of copper wires to link the house telephone to the provider through the public switched telephone network or PSTN. Internet can be implemented on the PSTN system, but it cannot run simultaneously with a telephone call. Since devices use digital signals and transmission is by analogue signals, a device called modulator-demodulator or modem device is used at each end-point to convert between analogue and digital signals. PSTN is still a popular telephony system because it is tried, easy to implement for a small outfit, and is not affected by power outages in the house. A simple setup will cost approximately $100 to $350 for one-user system, and $1200 to $1800 for a small office of less than ten users (voipreview.com).
ISDN
The integrated services digital network or ISDN is a development that transmits signals in digital form from end-point to end-point. The ISDN uses a digital PBX to connect and manage calls and internet. The digital system uses the same copper wires as the PSTN, but it can also use high speed Ethernet cabling, fiber optic cables, and wireless or radio signals to carry the signals. Digital phones are reliable, loaded with features, and have a high carrier capacity. The cost of installing a digital line and associated equipment is between $300 for a home-based one-station system and $5000 for an enterprise system. The pilot phone still works even when there is a power outage on the premises.
VoIP
VoIP technology is a digital signaling system that uses internet to carry voice data. Despite teething problems, the technology has become very popular because it is cheaper, integrated, not geographically limited, loaded with features and applications, has fast access, and can take many phone lines and extensions. If you use a separate internet and phone service then you can merge the two services into one integrated VoIP system. Be sure to have a high speed or broadband network and router, especially if you will have several phone lines and many users. Use a network speed test app to check the internet speed and latency. Compare various VoIP providers for price, plan, speed, and quality of connection. AT&T charges $23 for both traditional phone and VoIP with basic features, but $40 for just adding trunk calling. Not all providers support the 911 emergency number feature because VoIP works in a virtue and untraceable location. However, some providers have the Emergency 911 or E911, which the user configures with a physical address. It has to be reconfigured when changing physical address. Choose between the VoIP hardware and softphone for computer or mobile app, which can be installed as either a hosted VoIP, such as Tech Impact Hosted VoIP, or unified VoIP, such as BetterVoice and TechBridge. A DirectTV Choice Xtra plan integrates phone, TV, and internet at a total cost of $132.
VoIP used with IP-PBX is versatile, giving a wide range of features. It is sophisticated yet easy to use. It is also the most affordable integrated solution or unified communication system, and cheaper than separate telephony and internet systems. The VoIP PBX system is automated to filter calls to different extensions. It is also uniform and consistent in handling inbound traffic, therefore gives customers confidence and predictability in doing business with you. As the owner of the VoIP system you have full control of the service and its features, for example, the find me/ follow me feature.
Choosing a Digital Phone System
Whatever option and provider plan you go for will have implications on features and costs. The standard configuration will have a handset for each extension, the system PBX, and provider service plan.
Handset
A business needs a phone on every user desk. In a larger organization the system will have an extension and handset for each user. Each handset will cost around $40 to $80, but a cordless extension will cost around $150. In a small office outfit you can have a combo PBX-phone system in which each user has their own line and handset installed at a cost of $200 to $300.
Combo PBX-Phone System
For a residence or a small office with less than ten workers, a POT-based phone system with a line for each user may be adequate to install. For a bigger office you need to install a low-budget phone-PBX combo with two or four lines. . The combo phone system can have up to 12 lines and is not expandable. The PBX base unit with a cordless handset would cost about $700, and each corded extension handset would cost about $80.
The combo PBX-Phone has several advantages. It allows for an improved call quality that is not dependent on internet connectivity and broadband. The system works even without power and internet as the signals in the wires are powered by the provider. It gives a professional image as the company’s calls are centralized and forwarded to the appropriate department. It uses built-in menus, and its extensions are dedicated to the user at a desk. It supports emergency numbers since the PBX is at a physical location. On the flipside, the combo PBX system requires a technician to install and maintain it, which is expensive. The technician charges about $100 to $200 and needs two to five hours to do an installation. It is less flexible to scale and relocate, and needs extra equipment and wiring to expand.
VoIP Phone
VoIP or virtual system will not require a physical PBX, but rather an app or software called softphone. Whatever VoIP system option you choose, you have to consider the features like call forwarding, caller ID, conferencing, voicemail, and so forth. You can instead choose to have a medium-capacity PBX that costs between $1000 and $3000. In a standard plan you will be paying approximately $25 for each line. Alternatively, you can install a separate line for each user. It will cost you $1000 for the PBX, $80 for each handset, and $25 per month for each line and the PBX. The installation cost of a telephone system is approximately $250 for a two-hour residential job or $625 for a five-hour office job. If you intend to upgrade your system by expanding the PBX then you can purchase a line and extension card at a cost of $250 to $500. It is a good idea to replace the POTS system with a digital system or virtual PBX. It will give enterprise facilities like many extensions or users across the country or globe. Although you are familiar with phones and features, it is a different ball game when it comes to installation. You need a telephone technician or savvy person to install, maintain, and upgrade the system over its lifecycle. For a long term system you have to consider the support and backup. There is a possibility the provider will have closed shop, equipment become obsolete, and the installer left.
Enterprise PBX Phone
The legacy PBX, which costs nearly $10,000 to buy and $24,000 to install, is a physical box in a closet with line wires running into and extension wires out of it (voipreview.com). But the advanced PBX manages all communication channels, namely the phone, voicemail, fax, and internet. An enterprise PBX costs system costs around $1700 for wiring and installation, $2500 for setting up, and a monthly maintenance fee of $600. Annual maintenance could cost upward of $7200. The main contact line for inbound calls is called the pilot line. The PBX will therefore act as a virtual receptionist to auto-manage call traffic. Apart from connecting users to available external lines or extension lines, it identifies and blocks callers, monitors usage and cost of each extension, allows for call forwarding and holding at the touch of a button, and call recording. It also connects devices like the fax, telex, and the Internet, and forms an internal communication network.
Cloud-Based Phone System
The cloud-based phone system is an offsite digital phone system in which a third party manages your business communication system. The cloud host is either your phone service provider or a third party acting as a business process outsourcer. The cloud system is accessible, safe from viruses and malware, fault-tolerant, and affordable. Your digital phone system can be improved significantly when it is cloud-based. Cloud companies have massive servers and storage that are scattered around the globe and dedicated to the hosting of phone software and PBX. The provider hosts the PBX, audio-video conferencing, fax, call center, IVR, and data storage and access. The cloud-based phone system gives a professional-quality service, with fully loaded features and maintenance. It also enables you to maintain a presence in far-flung markets and at a low cost of mobility. Your business can therefore cut a larger-than-life profile. The cloud system gives you all the enterprise features at a low cost. It is flexible so that your agents and customers can communicate any time and from any geographic location, and with any communication device, at local or no charges. Used with helpdesk software, cloud-based phone system allows interaction between the agents and users using different platforms like social media, internet, and phone. While on the phone, they can exchange notes or files, gather information, and give personalized service. The business can also engage outsourced agents in places where they are not present.

The cloud system connects all the employees or agents irrespective of their geographical location. They have access to data and communication, and can hold a conference as though they were in one physical office. It is scalable because the lines are virtual. If you need extra lines and numbers you simply configure them. The system equipment is secure from failure and downtime because, first you do not need a physical PBX and software on premises, second, your cloud provider has a fail-proof system in which they have a number of parallel PBX phone servers distributed across the globe and running parallel. If one system fails the other system automatically takes over. Their massive broadband ensures there is less downtime, latency or delay in data packet delivery, and redundancy or instability or loss of data packets. Advanced security systems, like antivirus software, firewalls, and data encryption, reduce the threat to voice-data transmission.
The cloud host has the resources to upgrade their systems with the latest state-of-the-art technologies, in both hardware and software. Their multiple locations ensure excellent quality of service or QoS, and uninterrupted connections. Your business is spared the cost and trouble of upgrading their infrastructure, management, and maintenance of the phone system. Downtimes will only occur from the side of your premises or locations, and even then, the administrator can instruct the cloud PBX to redirect its communications to an alternative location.
Instead of buying software, you download the cloud provider’s software-as-a-service (SaaS). The cloud-based system is cost effective because it offers a wide range of virtual facilities and features at no extra charge, or at a nominal fee for out of network communications. The business benefits from innovations and upgrades of the VoIP system without additional investment, and often at no extra charge from the cloud host. Small businesses get superior, scalable, and secure services. Cloud-based VoIP is cost-effective when you have a large organization with multiple geographic locations.
PBX for Digital Phones
The physical or hardware PBX is a piece of equipment with a built-in facilities to connect lines and extensions. It directs the inbound and outbound flow of data and voice traffic. It routes incoming calls to extensions and devices within the business premises. Extensions can also be remote. It routes outgoing calls through the line to the public exchange. The modern IP-PBX can be a physical device at the premises, a hosted device at the service provider’s premises, or a virtual PBX in form of software at either the premises or the provider’s premises. The virtual and hosted PBX are popular among SMBs because they are much cheaper and offer the full range of functionality of the enterprise PBX. The hosted PBX is managed by the VoIP provider while the virtual PBX is managed by the cloud company. Owning a physical IP PBX is more expensive than hosted and virtual PBXs, but still a lot cheaper than the traditional PBX. For a growing company, you need an expandable system, especially the VoIP and PBX system. If you wish to minimize running costs, then you should install an integrated VoIP system.
PBX and Digital Phone
The private branching exchange or PBX is the common point of connection for inbound and outbound data and voice flow. It is used to route, transfer, and manage the in-house and external calls. Communications are routed through any of the available lines and to or from any extension. The basic features of a PBX system are auto-attendance, conferencing, voicemail and integration. PBX systems are designed to cater for both small, unsophisticated users and large, complex enterprises. The cost of PBX equipment varies from a few hundred dollars to thousands of dollars depending on the type and complexity of the system. The IP-PBX technologies allow for four types of PBX, namely, IP PBX device on premises, virtual PBX as a softphone, or hosted PBX with the provider, and cloud PBX hosted by a cloud host.
IP PBX and Digital Phone
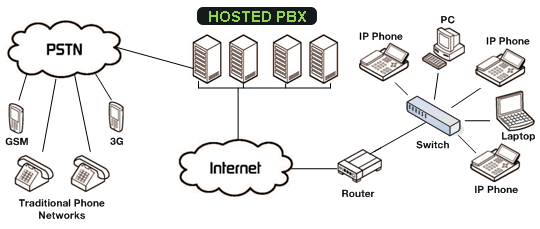
A simple physical PBX model such as the Panasonic KX-TG4500B for a small business costs approximately $250, while the BizFon costs about $400. It handles up to four lines and a dozen extensions. The extension handsets for the model costs $80 each. The PBX has a number of standard features like call forwarding, holding, music on holding, caller ID, and so forth. An enterprise PBX is a complex unit that handles hundreds of lines and thousands of extensions, with some extensions being remote or virtual extensions. The virtual and hosted PBX are popular among SMBs because they are affordable and offer the full range of functionality of the enterprise PBX. The hosted PBX is managed by the VoIP provider while the virtual PBX is managed by the cloud company. Installing an IP PBX device is more expensive, at $5000, than either a hosted- or a virtual PBX, at $3500, but it is still cheaper than the traditional PBX, at $6000. An organization may opt to install their own physical IP PBX using Ethernet cables and serving as a softphone server, such as the free, downloadable Asterisk. However it will need a techno guy to configure and maintain the PBX.
The Virtual or Softphone PBX
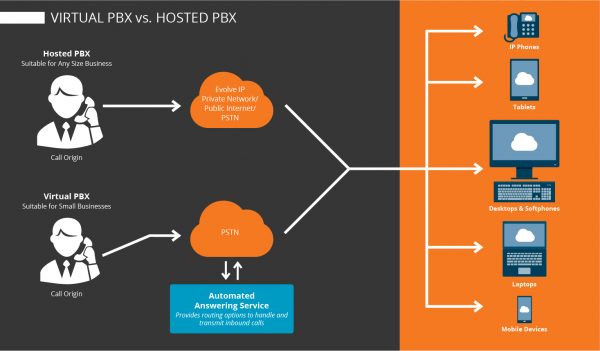
A virtual PBX is a software that mimics the physical PBX in managing the phone system. Normally, a high-end virtual PBX reserved for large organizations. A virtual PBX such as AvavaLive, Grasshopper, OneBox, and VirtualPBX.com uses built-in software to manage all communications. It has a visual display unit for the operator. The system allows incoming calls to be directed by the caller dialing an extension number. The PBX routes the calls to handsets, mobile handsets, answering machines, and even off-site phones that are mapped to the extension numbers. In addition the virtual PBX has voicemail, a phonebook, a facility to search and dial by name, call time limiter, among other enhanced features. The virtual software costs as little as $20 but the more advanced small business softphone costs about $150. A high-end virtual PBX such as ShoreTel allow advanced management of a large company’s communication system, using softphone software installed on a computer.
The Cloud-Based PBX
Imagine the handicap you face when your business communication system breaks down and you cannot call, use email, text, chat, or collaborate. You need the fail-proof cloud solution. The cloud system is really a hosted PBX where the physical infrastructure is owned by a third party – the cloud provider. The cloud PBX system has the same features and pricing structure as the hosted PBX, but the cloud host is really a third party business outsourcing provider rather than a VoIP provider. The cloud-based phone has gained popularity because it gives advanced features to an SMB who may otherwise be unable to afford their own advanced system. You can use a remote online location, called the cloud, to perform tasks like PBX, VoIP, texting, calling, file storage, running software, and so on. The cloud service has more features, better disaster recovery, state-of-the-art technology, and is easy to upgrade. The cost of implementing the cloud system is quite low because it does not involve buying new equipment, while the monthly fees are comparable to other VoIP phone systems. In fact, the rates are low for international and long distance calls. From the user’s point of view, the hosted or cloud PBX is the easiest system to implement and maintain.
Cost of Installing the Digital Phone System
VoIP Phone System for the Home and Small Business
Upgrading the home analogue system to a VoIP system is simple and affordable. You need at least an analogue telephone adaptor or ATA, router, modem, and broadband. The ATA optimizes the home phone for VoIP instead of replacing the phone with an IP phone. It costs $15 while an IP phone costs $100. The router carries signals between the device and the telephone line, and costs between $30 and $200 depending on its speed, quality and capacity. Providers like ITP include a free adapter and router in their monthly plan.
Cost of the Router
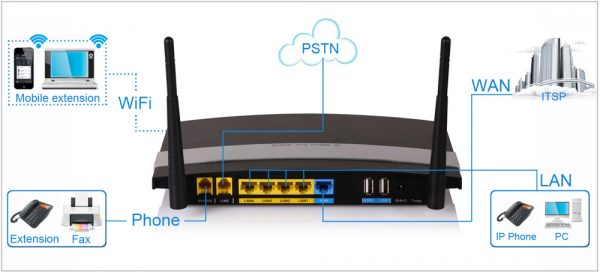
The cost of the router depends on the number of connections, speed, range, whether it is a narrow band or broad band type, reliability, and extra features. The cost ranges in the $20 to $200. Some common routers are listed below;
| ROUTER MODEL | COST | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| Netgear Rangemax | $21 | It is low-priced, supports Skype and Vonage, and UC, but has poor signal, is slow, and prone to breakdown. |
| Netgear AC1750 | $129 | It can handle multiple and wireless devices, supports Skype and Vonage, and UC. It is fast with its 1.75 Gbps bandwidth and 802.11ac Wi-Fi, but it drops signals. |
| TP-Link Archer C7 | $94 | It has good performance and speed of 1.75 Gbps bandwidth, and 802.11ac for Wi-Fi. It supports Skype and Vonage, and UC, but it drops signals. |
| ASUS RT-AC68U | $191 | High-end features like 1.9Gbps dual band Gigabit and Wireless-N router that boost data speeds by 33 percent. It is expensive. |
The modem, short for modulator-demodulator, converts between digital and analogue signals. Devices are digital while the transmission is analogue. The modem costs about $75. You will also need to upgrade your broadband to accommodate the higher demand for VoIP services, which include digital telephony, internet, and cable TV. Digital phones are top heavy on broadband usage, especially when you include conferencing and video calls. Broadband internet cabling costs between $80 and $400.
Connecting the Phone Line
Sharing the digital line for VoIP and Internet in a busy company even with high bandwidth leads to poor quality calls, including call dropping and distortion. It is better to have separate dedicated lines. Having a separate internet and VoIP providers is tricky because it negates the cost advantage of having VoIP. Dependence on the phone company for VoIP is more expensive because their rates are related to duration of usage. Internet is more fault tolerant than VoIP since a glitch in the line leads to a call drop whereas the internet can reconnect automatically. If you have few users then each user will need at least one line and you need a spare line for a call-waiting service. If you have many users then you need fewer lines than the number of users, but enough to serve the peak demand. The monthly plan for VoIP costs between $75 and $200 per month, depending the plan, and which may include sharing the bandwidth with cable TV and other communication add-ons.
A network technician will charge between $100 per hour and take between three and eight hours. For basic VoIP call and internet services you will choose a low-budget provider such as Skype for $2 per month or Vonage Business for $40 per user per month. They allow unlimited international calls to over 60 countries. For high-end features you can subscribe to a hosted PBX phone provider at between $20 and $100 per user. There are minor charges like an extra number for $10 to $20, toll-free number for $10, number porting for $5 to $15, and taxes.
Cost of Upgrading the Digital Phone System
If you are a light user, for example a home or SMB user, you should stay with the older non-KSU or dial up system which costs less than $300 to install, $20 for an extension, and $30 for a standard monthly plan. For a heavier user, there are three main options of digital phones, namely; the key system unit or KSU, private branching exchange or PBX, and voice over internet protocol or VoIP. The digital phone system can be implemented either on a public switched telephone network or PSTN, or on an integrated services digital network or ISDN technology. The PSTN is analogous while the ISDN is digital. The choice of a digital phone system depends largely on the size of the business, the demands on communication, and budget. The cost of installing the system depends on the type of phone system, number of lines and extensions, complexity, and needs of the business communication system. Homeadvisor.com notes that the national average of installing a telephone system is $400, while the range is from $75 to $1200. A new PBX system would add between $800 and $5000 to the cost. Each extension handset costs about $80 to buy and configure.
Cost of KSU
The KSU is a centralized control unit to support several lines and up to 40 simultaneous users. It allows simple functions like call forwarding, hold, and transfer. The system costs between $400 and $3500 for the KSU, between $80 and $200 for installation of each extension, and between $200 and $1000 for labor by the phone engineer.
Cost of PBX
The PBX system is essentially similar to the KSU, but with more capacity and functionality. Telephone lines and extensions are connected to, managed and controlled by the PBX automatically. A console helps the administrator to configure the system. Installation costs $1000 to $10000 for the PBX equipment, $80 to $200 for each extension, and $500 to $10,000 for labor (voipreview.com). Each extension has full features like a display unit, voicemail, email, storage unit, and so on.
Cost of VoIP and internet
A VoIP system is a cost-effective system that uses a high-speed internet connection to for both and data and calls. It supports video calls, online and real time collaboration, among a host of other functionalities. It is ideal for all sizes of business. The system is cheap to install, with a VoIP box costing $200, and even to cheaper to subscribe to compared to the other systems. Functionality is software-driven, and can run on a mobile device such as a mobile phone, laptop, tablet, or smart phone. When added to the PBX the VoIP system can cost up to $4000.
A simple VoIP system with either a handset or a mobile phone costs between $175 and $250 to install. It offers advantages over the traditional analogue system, for example trunk and international calls at minimal charge. An SMB and residential VoIP is designed for light use on low-budget, so it requires a medium broadband worth between $500 and $2000 to install. The following bandwidths are a guideline for call-based services as a minimum;
| CONCURRENT CALLS | RECOMMENDED UP/DOWN SPEED | MINIMUM BANDWIDTH |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 Mbps | 100 Kbps |
| 3 | 3 Mbps | 300 Kbps |
| 5 | 5 Mbps | 500 Kbps |
| 10 | 5-10Mbps | 1 Mbps |
The enterprise VoIP is designed for large organizations with complex communication needs and a budget to match. Its users are scattered widely, and therefore have virtual extensions which $30 or so to maintain monthly. The system links multiple locations to a local base through internet. Since a VoIP system requires power supply, you need to install a power backup system, such as a battery, generator, or an uninterruptible power supply or UPS. A generator will cost about $500, a battery pack will cost $400, and small UPS will cost about $60 to $200.
Cost of Cabling
According to voipreview.com, upgrading the home analogue system to a VoIP system is simple and affordable. You will get broadband internet cabling for between $80 and $400. A network technician will charge between $100 per hour and take between three and eight hours.
Cost of Power Backup
Since a VoIP system requires power supply, you need to install a power backup system, such as a battery, generator, or an uninterruptible power supply or UPS. A generator will cost about $500, a battery pack will cost $400, and small UPS will cost about $60 to $200.
Cost of Implementation and Monthly Plan
According to voipreview.com, upgrading the home analogue system to a VoIP system is simple and affordable. You will get broadband internet cabling for between $80 and $400. A phone system engineer will charge $200 per hour and take between three and twelve hours to install. There are minor charges like an extra number for $10 to $20, toll-free number for $10, number porting for $5 to $15, and taxes.
VoIP Phone Services
VoIP Phone vs. Digital Phone System

The digital phone system transmits signals digitally, and can use traditional wiring to transmit, while VoIP is a technology that transmits voice using the internet. Internet, and therefore VoIP, works on both analogue and digital transmission. Although VoIP and digital phone systems are technically different, the terms are used interchangeably to mean phones that work with digital transmission. Both are similar in performance and therefore choice depends on compatibility, budget, reliability, and desired features. The digital technology is older than VoIP, but both can work with the preexisting analogue system. Digital is a time-tested, reliable, stable, and cheaper system to implement. VoIP drops calls intermittently when the internet is slow or unstable. Its calls are cheap because they are treated as part of internet use, while digital phone calls are more expensive because they are treated as regular calls. VoIP is mobile because you can access it from any location with an internet. It also has many features, such as a user-friendly interface, number porting, call forwarding, and so on. A digital phone system is tethered to a physical location, has limited features, and transmits audio data, but VoIP transmits data and internet protocols. The VoIP phone relies on the power of Ethernet or PoE unit for power and the computer running, while the digital phone relies on the exchange for power and works even when the computer is off. Finally, VoIP is easily maintained even remotely and without downing the system, while the digital phone requires physical presence of a technician and shutting down the system for maintenance.
Reasons for Switching to VoIP Phone

Typically, people who switch to VoIP save about $50 a month on telephone bills, according to Consumers Report. Long distance and international calls become cheaper as they are charged at nominal rates or come as free. For example, in their Global Plans, ITP offers unlimited calls for $25 while Jive has a nominal charge of $0.03 per minute. Advanced calling features are usually offered for free. Some features are innovative, for example the ability to email a voicemail file. You can obtain virtual numbers in different towns for localizing the calls in the selected areas. VoIP is convenient because you can use it the same way as you do with the traditional phone. In addition you can track your calls, change your account information using an administrator portal. Finally, VoIP is mobile as you can access it from anywhere in the world. You can also have mobile VoIP in your smartphone (voipreview.com).
Although VoIP has many features, you likely will use only some of those features, especially the ones with no additional costs. Many VoIP providers have plans to fit all pockets among the residential, SMB, and enterprise users. All users basically need VoIP for calling, internet, and TV. A residential user may require video calling but not conferencing and call forwarding. An SMB may require call forwarding but not virtual extension, and an enterprise may require most services. The common features for each type of user are tabulated below;
| TYPE OF VOIP USER | ENTERPRISE ONLY | ENTERPRISE AND SMB ONLY | ENTERPRISE, SMB, AND HOME |
|---|---|---|---|
| FEATURE | Virtual Extension | Conference Calling Video Conference Do Not Disturb Group Hunt On Hold Music Group Paging Auto Attendant Simultaneous Ring | Call Notification Caller ID Dial by Name Voicemail Call Waiting Video Call Find Me/Follow Me E911 Number Porting |
Apart from the mainstream systems, there are other less common systems. An IP phone system allows several handsets sharing a single line. SIP trunk systems allow any number of handsets but a limited number of simultaneous calls. It can be set up and activated remotely by the provider.
Choosing a VoIP Phone Provider
In order to get the best VoIP service you need to compare providers for features, reliability, and prices. Do your research beyond the embellished ads and reviews, consult with other consumers, and visit a few providers. Read the technical literature, helpful articles, and independent user reviews and blogs. Remember that some mainstream blogsites can be biased. If still in doubt, then stick with the time-tested providers. Naturally, you should. Determine how often you would like to use the internet, phone, email, conferencing, text, chat, and other services, so that you can choose the most appropriate plan for you and your budget. You also have to choose the right PBX for you, be it hosted, IP-based, or cloud-based PBX. An offsite PBX will save you the cost of equipment and installation.
Advantages of a VoIP Phone System for SMB
The VoIP for SMB and home use is cheap to install because it only requires a compact PBX and softphone. A small capacity softphone is either free or cheap at less than $100. An enterprise VoIP infrastructure costs from $1200 and can reach $10,000. VoIP is a cost-effective solution for regular calling, especially to long-distance and international destinations. The VoIP phone system is versatile. It can do a wide range of value-added services. You can connect to external calls from any extension via any of the available lines. Calls can be monitored and logged on the console, and you can limit access by use of password. The system allows such services as voice call, voicemail, recording, email, texting, teleconferencing, and internet. You can do multiple activities while still on the call. VoIP services are scalable in capacity and range to suit the growing needs of the business.
The system is mostly maintenance-free. The service providers give several flexible options, which include residential plans that cost between $3 and $60, and business plans which feature advanced facilities at between $10 and $80 per user. The VoIP is a software-driven control and management system that combines the various digital communications into a seamless integrated VoIP service. It is the ideal system for SMB and homes. VoIP is particularly popular because it has facilities that make it interactive in real time. For example you can connect to a printer or fax machine for remote jobs. A document can be sent from an offsite location and printed directly to the printer. You can receive or send an email through the computer, tablet, laptop, smartphone, and even smart TV. You can also send and receive text, voicemail, and instant messages. VoIP gives small companies a platform to advertise themselves, thereby boosting their profile and business flow. This is so because through the call waiting facility, the VoIP is able to deliver advertising messages, and with help from analytical software, the helpdesk can be set to automatically send messages and promotions to selected customers. Calling rates are a lot cheaper. On the one hand, an AT&T monthly VoIP package costs $35 and internet costs $15. Other VoIP providers are even cheaper than AT&T. On the other hand, a monthly telephone-only plan cost $50 or more per line.
VoIP drives competition in SMBs. Firstly, providers compete with each other for the SMB segment, which drives down the cost of VoIP phone plans. They have competitive plans like lower prices, discounts, value-added features, and free IP. A money-back guarantee gives the VoIP consumer confidence in the service provider. Secondly, SMBs benefit from affordable and professional VoIP services which give them a competitive edge over their non-VoIP rivals.
Hosted PBX
This is the scenario where your phone service provider manages the phone system on your behalf. They connect you to agents in the office and afield. A hosted PBX is a cloud PBX. Your business does not have to be experienced in VoIP phone management, but instead your phone company will do it professionally and leave you to focus on the business itself. You also do not have to own an IP PBX phone system at your premises, but instead you rely on the provider’s PBX. As a result you are able to save money on PBX and VoIP equipment investment. For a nominal fee the VoIP host provides you with a system that has advanced features normally reserved for large businesses. The hosted provider gives you flexibility in choosing the right plan, that is, limited or unlimited, and metered or unmetered plan. The metered plan sets a limit on number of minutes of use. It is the cheapest plan that is best suited to infrequent users. The hosted PBX plan allows you to add and remove phone lines by a simple click, since the lines are virtual rather than physical. The hosted PBX creates virtual offices which have exactly the same accessibility wherever they are accessed from. The find me/follow me feature forwards calls to a predefined number, which is normally a portable device such as a mobile phone, tablet, fixed phone in another location, or laptop. With the find me/follow me feature you can reject calls using the DND feature.
Setting up a VoIP
For an effective VoIP you need to ensure the network, equipment, and software, where used, are properly installed. You then check the internet bandwidth to be sure it meets the threshold for high speed, low latency, and uptime (uninterrupted service). A split second glitch will result in a dropped call. Voipreview.com advices that you upgrade your bandwidth and VoIP box if necessary. Make sure your LAN is set up for VoIP. Review your usage of the internet and telephone, and project how that usage will increase or decrease in the near future, then use the knowledge to select the right plan for you. If you often make non-local calls or engages a lot in customer enquiries then you will need VoIP. If you have a PSTN (landline) then you might not require a power backup, but you must have it for an ISDN system. You need to also determine if you will have a premises-based system or a provider-hosted system. The premises-hosted system costs more to buy, install, and maintain the equipment and software, but less on the monthly plan. You have to buy your own PBX, power backup unit, and VoIP box. A hosted system is cheaper and faster to implement, up even during power outage in the office, and it removes the hassles of managing the system. However the convenience comes with a price tag. Choose the VoIP provider who will give you good value for money, including low rates, high bandwidth internet, low latency, and a near-perfect uptime of at least 99 percent. Seek a plan that is tailored to your needs as a residential user, or SMB, or large organization. At the end of the day you need to balance your budget for VoIP services as opposed to the older internet and telephony system. Some providers offer discounts on long-term plans, for example, RingCentral offers a 33 percent discount if you make an annual payment instead of a monthly payment.
Helpdesk for Digital Phone System

The helpdesk software, aka softphone, is a software that enables the user to work with IP phones. There is a long list of helpdesk software for every situation, size of business, and budgets. The basic features expected from any helpdesk are ticket management, connectivity, and hosting. In ticket management, the helpdesk generates, edits, and closes a customer support issue. The ticket is edited as issues are resolved, and closed after all issues have been resolved. Tickets are queries that can be created from calls, email, and social media. They are either manually initiated, or automatically created. Functions include prioritizing, categorizing, assigning, and tracking. The tickets should be used to build a knowledge database of issues and solutions. Tickets are assigned to appropriate teams and active members in a round robin manner. Tickets can be escalated to a higher service level.
The softphone allows a customer access to the knowledge base for answers to FAQs, blogs, and surveys. The system keeps track and count of the popularity of communications on social media and phone calls. The helpdesk also adheres to information technology infrastructure Library or ITIL. ITIL is a set of best practices in procedures, tasks, processes, and checklists that ensure the phone system works efficiently and effectively. FreshService and ServiceDesk Plus are ITIL-compliant helpdesks. Compliance is more costly on the software purchase, but it offers great savings in business communication. ITIL non-compliant helpdesks such as Cayzu, Freshdesk, ZenDesk, and HappyFox are cheaper and more suited to less complex businesses. The ITIL reporting feature does live reporting using data from the knowledge base and ongoing activities. It should report on staff performance, ticket flow, and issues resolved. With the helpdesk you can integrate all communication services such as calls, conferencing, broadcasting, email, social media, database, spreadsheet, and so forth. For example, the call answering app Twilio works with the softphone HappyFox to automatically generate tickets based on customer answers to prompts. While Twilio transcribes the voice into text, HappyFox generates tickets. Softphones can integrate with accounting software like Intuit Quickbooks, and CRM like Salesforce and SurveyMonkey. The helpdesk also communicates with other apps. Ticket data that has been collected and analyzed is availed to other system users, who then come up with solutions to problems, conduct research and analysis, and educate agents on how to resolve customer issues. The agent has access to technical information and solutions on the CRM database. HappyFox has a ticketing feature specially designed for SMBs, while Vivantio Pro and Zoho have ticketing features designed for enterprises.
Comparison of Helpdesk Features and Costs
The PC Magazine has compared the features and costs of a number of helpdesks, and the finding noted below;
| SOFTPHONE | MONTHLY COST/USER | FEATURES |
|---|---|---|
| Vivantio Pro | $60 | Rich in features. |
| HappyFox | $19-$69 | Intuitive automation and self-service tools for tracking |
| Zoho | $25 | Flexible and suited to SMBs. |
| Agiloft Service Desk | $65 | High-end features, but requires a lot of configuration. |
| ServiceDesk Plus | $395 | High-end features and has asset management function. It is expensive. |
| Freshdesk | $16 | User-friendly, with few advanced features. |
| FreshService | $16 | Streamlined and intuitive, but few ITIL features. |
| Zendesk Support | $5 | A basic, low-end app for ticketing. |
| Jira | $10 | Good features but lacking in knowledge base and social media support. |
| Samanage | Trial | A basic app |
| Desk.com | $30 | Good for producing and closing tickets only. |
| Cayzu | $12 | Generate tickets from social media. |
| Mojo Helpdesk | $1 | An entry-level app with just basic features. |
| Kayako | $20 | Enterprise security, user-friendly, and multiple communication channels. |
| Teamwork Desk | $ | New and still developing |
| TeamSupport | $35 | Good but outdated interface |
| Revelation | $45 | Good capabilities in filtering, search, and reporting. |
Cheat Sheet: Digital Phone System Terms
Audio and Video Jacks
The sockets that allow audio and video devices to be connected to each other, for example a computer to be connected to a headset.
Bandwidth
The amount of data that a communication device is allocated to send or receive in a second. When a large bandwidth is allocated then is called a broadband.
Caller ID or Calling Line Identification
The service that enables a recipient to view the number or name of the caller before receiving the call. The receiving phone has to have a digital display unit. It also allows one to automatically reject a call from a blocked caller ID. In the older landline telephone systems this is a paid service at the rate of $3 to $10 per month.
Communication Panel
This is the panel from which the house communication, environment, and security system is controlled. The panel is linked to sensors and devices either via a data cable or a wireless cable. The security panel costs around $1,800 to install and $500 in annual fees.
CRM
The customer relationship management feature is used in the VoIP system to improve interaction between the customer and the business.
Ethernet
The Ethernet is a local area network (LAN) connectivity system that often uses a twisted pair of cables or optic fiber.
IP
The Internet Protocol or IP is the set of rules for exchange of data including connectivity and security, often called handshake, within and between internet systems.
IVR
The interactive voice response is an automated system to answer customer queries. The customer responds by pressing option keys.
PBX Phone
The private branch exchange (PBX) is a digital phone system that has such features as call waiting, extension lines, routing, and hold, and it can be connected to the internet, public switched network, session initiation protocol or SIP, VoIP, and trunk service providers.
Router
The router is a switch that receives or sends data between your system and the provider. A router can support between 4 and 48 connections, but top-heavy router can take hundreds of connections.
Softphone
The PBX and telephony software that used in a computer or as a mobile app. Softphone replaces the physical PBX to manage the telephone system.
UC
Unified communication is the merging of all internet and telephony services into an integrated service.
VoIP or Internet Phone
The Voice over Internet Protocol or VoIP is a technology that enables the use of the internet for telephony communication. The quality of VoIP calls, for example Skype and Vonage is usually lower than a conventional phone. Since it works as part of internet communication, the cost is usually the same for local, long distance, and even international calls.
Sources:
voipreview.com
homeadvisor.com
